厚朴(MAGNOLIAE CORTEX)安全性文獻回顧

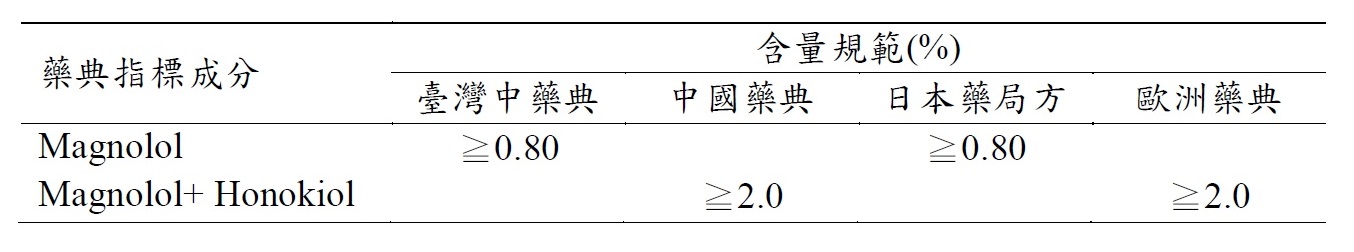
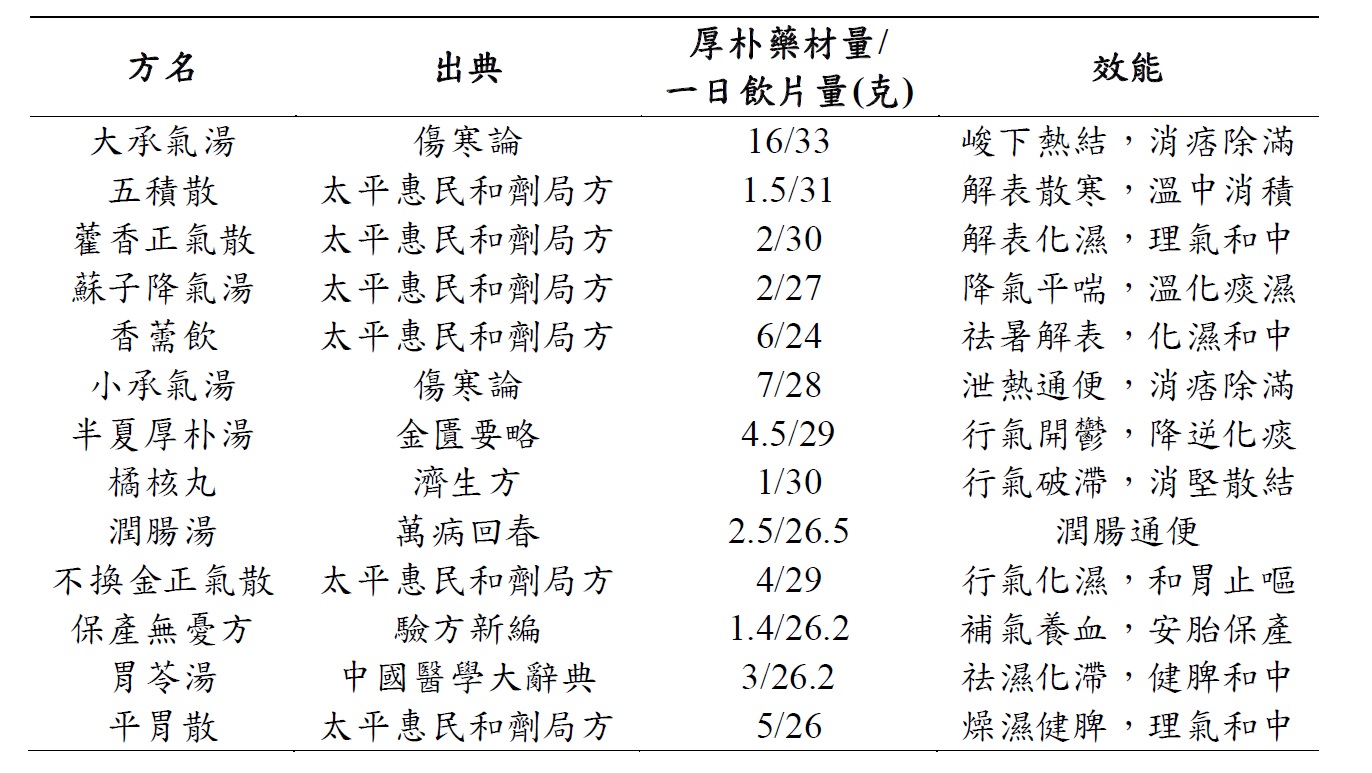
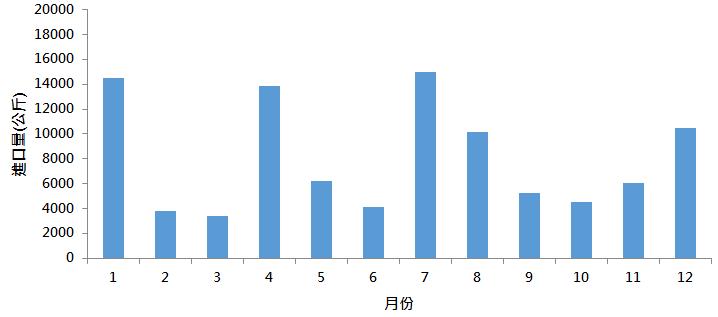
依據臺灣衛生福利部中醫藥司網站統計資料[1],厚朴於2019年總進口量為97,357.7公斤,每月皆進口至少3000公斤的厚朴藥材(圖一),再次顯示厚朴於臺灣中醫師開立處方之重要性。
- General: No information was found.
- Drug interactions: None reported.
- Drug and laboratory test interactions: None reported.
- Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis: An aqueous extract of the bark was not mutagenic in the Ames test in Salmonella typhimurium strains TA98 and TA100 at concentrations up to 40.0 mg per agar plate.
- Pregnancy: teratogenic effects: None reported.
- Pregnancy: non-teratogenic effects: Due to a lack of safety data the use of the crude drug during pregnancy is not recommended.
- Nursing mothers: Due to a lack of safety data the use of the crude drug during breastfeeding is not recommended.
- Paediatric use: Due to a lack of safety data the use of the crude drug in children under the age of 12 years is not recommended.
- Adverse reactions: No information was found.
- Traditional use contraindicates.
- Traditional use as an abortifacient or uterine stimulant.
- Relevant adverse event data in humans exist and have probability of causality.
- Data in animals suggesting teratogenicity or other adverse effects on the fetus or mother, with reasonable application to humans.
- For plants with common food uses, standard dose is in excess of typical food amounts.
- https://dep.mohw.gov.tw/docmap/cp-4747-38404-108.html.
- 劉崇喜,建立厚朴中藥材飲片炮製基準及炮製廠規範(CCMP93-RD-070),2007。
- Liu et al. Evaluation of short-term and subchronic toxicity of magnolia bark extract in rats. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 49, 160-171, 2007.
- Li et al. Evaluation of the in vitro and in vivo genotoxicity of magnolia bark extract. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 49, 154-159, 2007.
- Zhang et al. Evaluation of magnolia bark extract in chromosomal aberration assays. Mutation Research 654, 133-137, 2008.
- Kalman et al. Effect of a proprietary Magnolia and Phellodendron extract on stress levels in healthy women: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutrition Journal 7, 11, 2008.
- WHO monographs on selected medicinal plants. Volume 4, page 167-178, 2009.
- American Herbal Products Association’s Botanical Safety Handbook. Second edition, page 539-540, 2013.


